Title: 3D Stent Recovery from One X-Ray Projection Paper Link
Authors: Stefanie Demirci et al.
Association: Computer Aided Medical Procedures, Technische Universit at Munchen, Germany
Submission: 2011
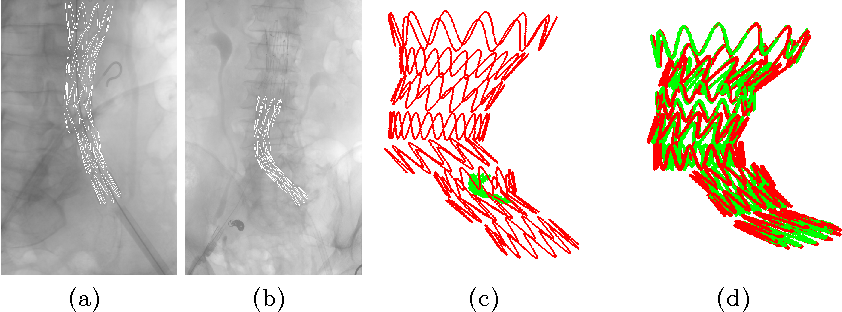
Image registration is a key component for medical image analysis to provide spatial correspondences.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
»> Background of Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis
»> A Review: Robot-Assisted Endovascular Catheterization Technologies:
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
»> Image Registration Basic Knowledge
»> Image Registration Literature Review
»> Slice-To-Volume Medical Image Registration Background
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Motivation
stent graft 3D visualization within the CTA volume would provide the physician a 3D view of the current situation. This mixed view can help ensuring the correct positioning of the stent in regard to his planned measurements. —> increase extensive use of contrast agent and the radiation dose.
Contributions
(0) a novel algorithm to match a 3D model of the stent graft to an intraoperative 2D image showing the device.
(1) stent graft detection in 2D and correct backprojection into 3D
Stent Model


[My stent 3D model code (matlab)]](https://xuuuuuuchen.github.io/)

Methods – Automatic Feature Extraction
employ the Frangi filter for scales 5 − 6 followed by a median filtering for noise removal in order to capture the catheter pixels.

-
subtract thick curvilinear structures from thin curvilinear structures (Frangi filter for scale 2) for only highlighting the stent wires
-
a median filter for noise removal and mean filter for dominant region extraction leads to the desired image region that contains the stent graft.

Methods – Stent-Model-to-Image Registration

Loss Funciton

Global registration


The global pose of the entire stent graft model is defined by the global parameters:
-
K (4-DOF intrinsic camera parameter)
-
R_global : α_global, β_global, γ_global (Rotation)
-
t_global: tx_global, ty_global, tz_global (Translation)
Where γglobal and* tx_global, ty_global* can be estimated from the stent region S via principal component analysis (PCA) and center of mass detection.
SO
only rotation around the camera’s x- and y-axis and translation in along z-axis need to be optimized.
define P_global = {α_global, β_global, tz_global}
And then,

Local registration
Loss Funciton

WHERE,

; In order to account for small measurement errors, an additional parameter λ was added to the penalization equation

Performance
